The Technology Paradigm Constituting the Mobile Ecosystem

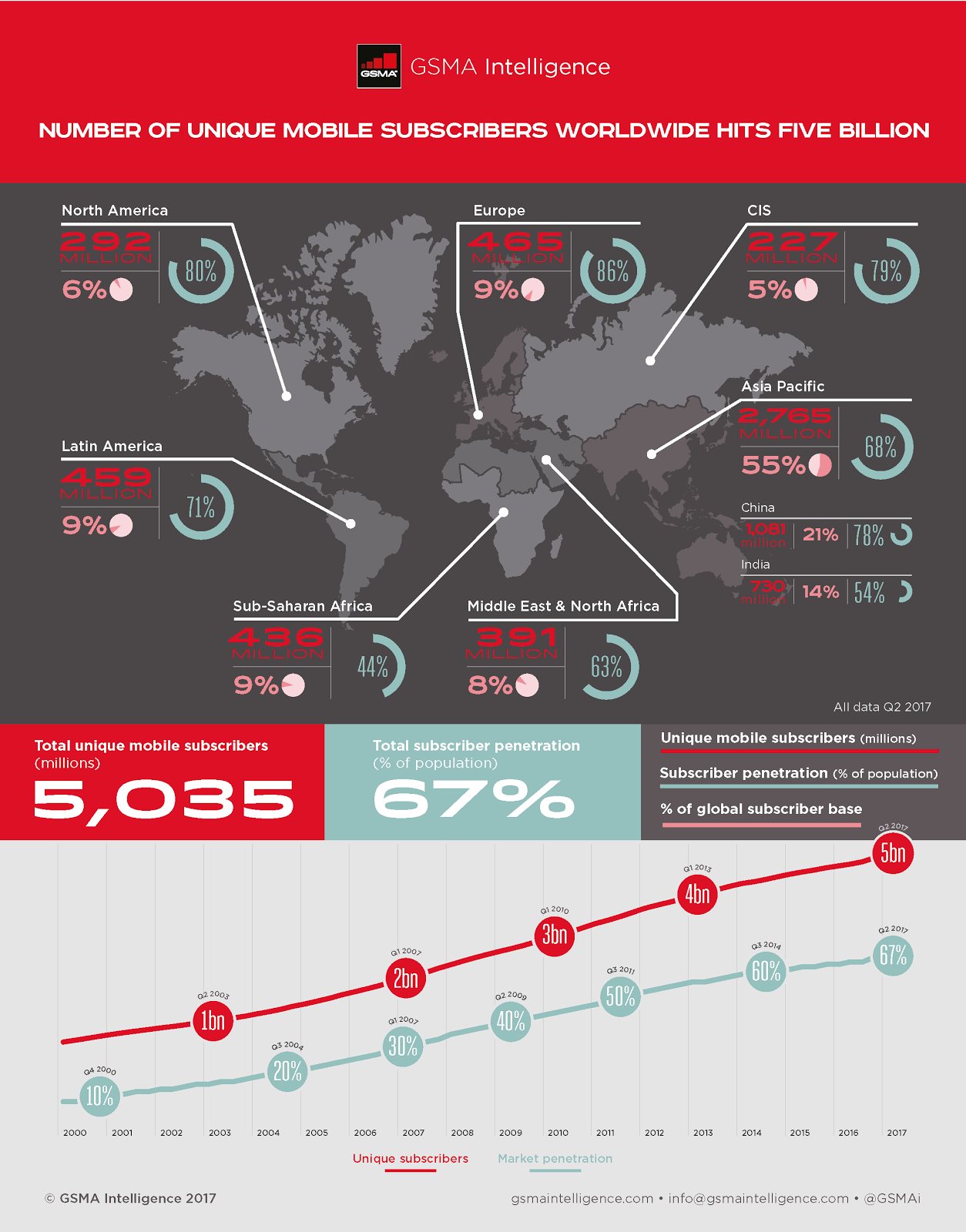
A recent GSMA report features that two-thirds of the world’s population are now mobile subscribers. Approximately 5 billion people have a mobile connection while recognizing its potential as a versatile platform to access global mobile solutions and technologies.
The Emergence of Internet Data Traffic
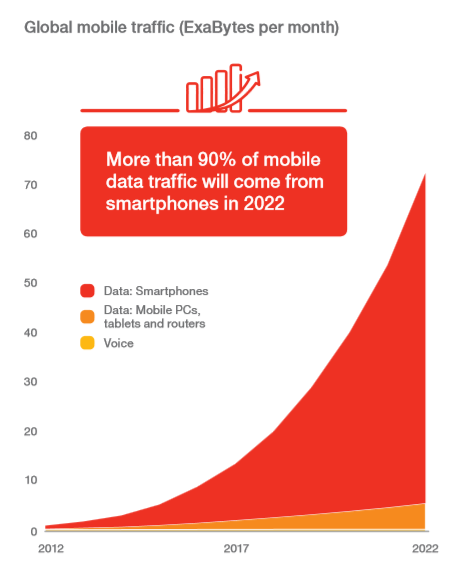
Mobile has become a gateway to the vast amount of services and applications available on the cloud. With each subscription, every individual increasingly becomes aware of the possibilities that internet offers. As a result of which, there has been a 70 percent increase from Q1 2016 to Q1 2017 (Ericsson reports).
The Smartphone Symbiosis
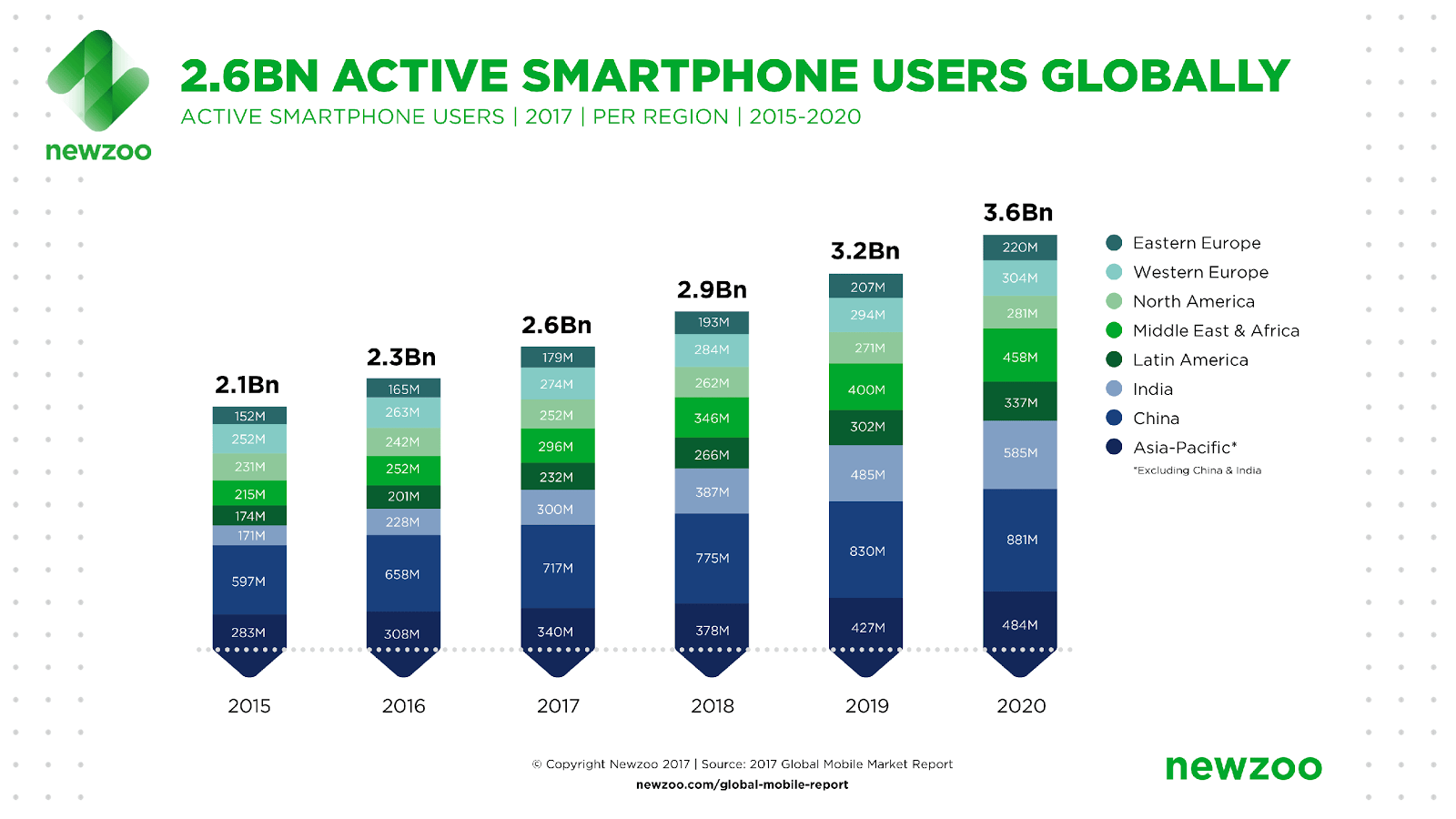
GSMA shows us that smartphones account for over half of total mobile connections globally. It is mostly the emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Africa, MENA, etc., which are experiencing faster smartphone subscription as compared to affluent markets.
Despite lower penetration, smartphone subscription in developing economies is set to skyrocket, especially in the more populated regions like Asia-Pacific and Africa. Therefore, we can expect more than a billion people using mobile to access the internet by 2020 (GSMA report).
One can conclude from these facts that the increase in internet data traffic is happening in tandem with higher mobile/smartphone subscription. Smartphones are more adaptive to higher data volume and support plethora of applications over the cloud that most users.
The Rise of LTE networks
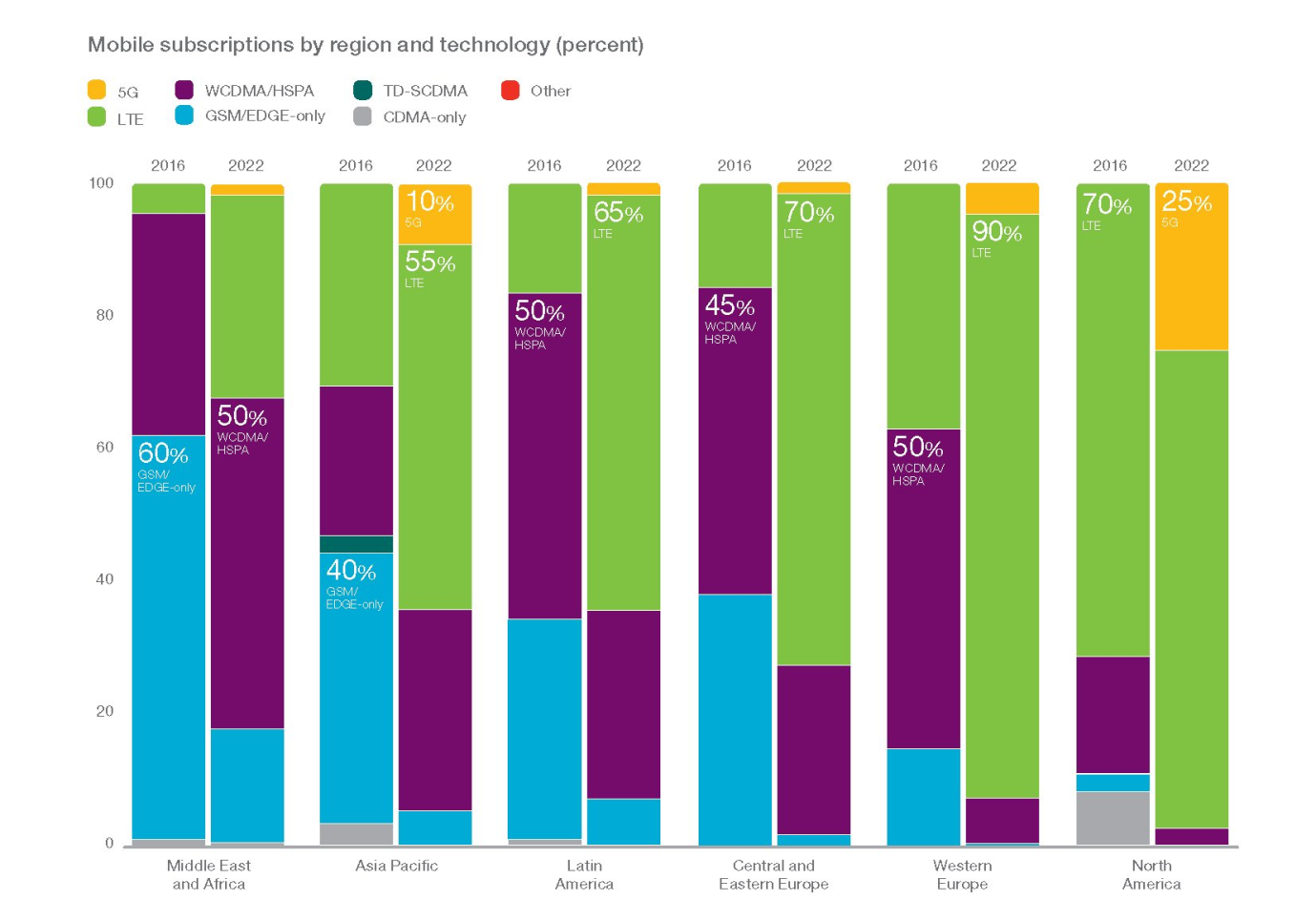
Increased internet data traffic is being attributed to the rapid uptake of LTE network connection. LTE has fundamentally reconfigured internet access by mobile phones. It is easier for LTE backed devices to navigate faster while seamlessly browsing multiple websites and cloud-based applications.
As a result, there has been a massive difference in the way people connect over their devices. There is an increasing shift towards cloud-based mobile experience, which is being powered by LTE technology.
Faster Deployment in Emerging Economies
We are well aware that most of the population across the world is still in the process of embracing 4G network with higher penetration in developed economies. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are set to represent 35 percent of the 4G increase and lead to a geographic shift in internet users (GSMA)
With more than 540 million people estimated to switch over to an LTE network by the end of 2017 (Ericsson), the mobile industry is gearing up for a simultaneous growth in the global internet data traffic. There will be an overall transformation in the telecom space with mobile increasing becoming a means to meet dynamic ends beyond communication.
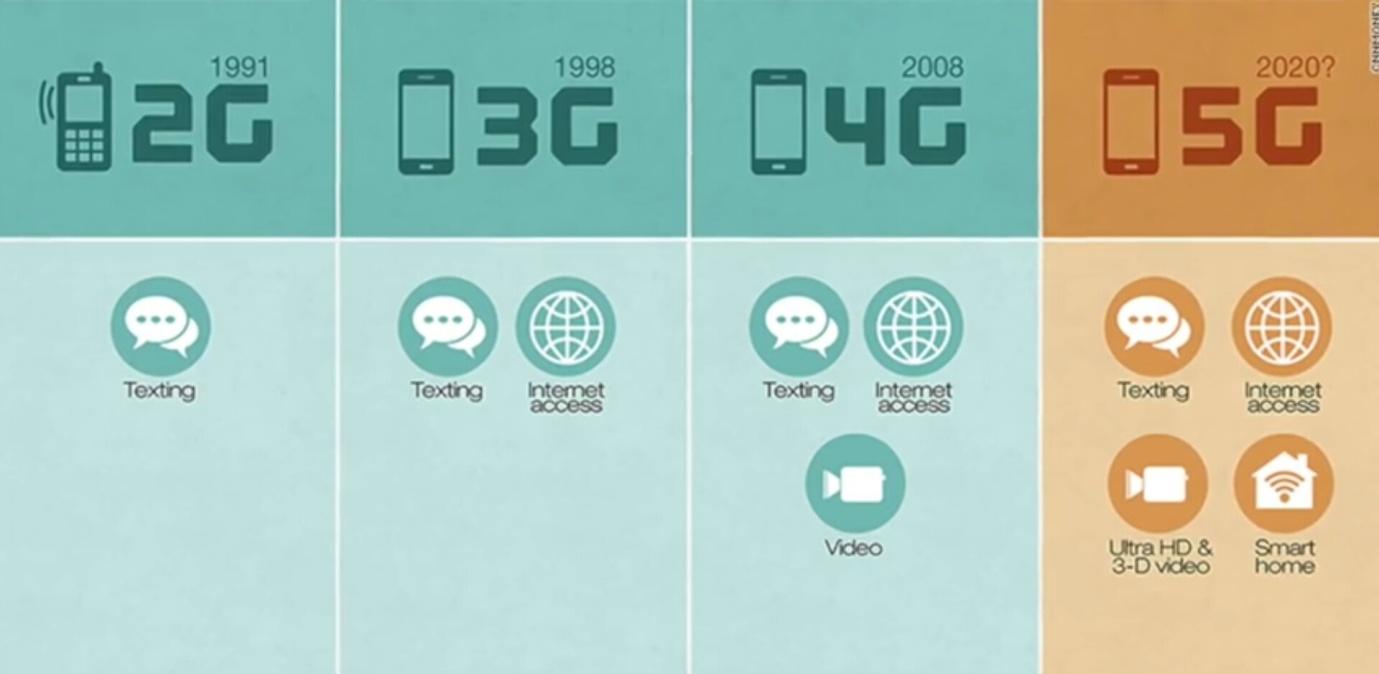
5G and the Advent of Connected Devices
With LTE networks gearing up for further evolution, the 5G network is on the rise and estimated to take over by 2020 (Lanner-America). The 5G technology promises higher speed and faster data transfer. Hence, it is a move towards boosting the network of connected devices while allowing more devices/objects to exchange data and avoid over-crowding.

Implications for Voice Communication
There is no doubt that 5G or more robust LTE is exponentially going to enhance our experience of communication. VoIP will mainly reap the benefits of a 5G upgrade while avoiding ‘packet’ loss and poor network connectivity that 4G is yet to overcome. This will be made possible because 5G will exceed 4G’s threshold of data upload.
Enterprises will primarily be at the receiving end of these benefits. Apart from having multiple connected devices in a business environment, they will also avail improved video conferencing, daily business operations assisted by virtual and augmented reality. This will be entirely executed minus the delays in the network.
Need for Robust Infrastructure
The deployment is also set to significantly improve coverage in remote areas and inside buildings because of multiple transmitters and receivers spread over larger distances. To achieve this, there has to be a consolidated focus towards uniformly developing network infrastructure across all regions. As per Ericsson report, more than 50 percent of our population does not have internet access due to poor access and economic constraints.
Mobile will continue to be the focus of cumulative technological development. It laid the foundation for a plethora of innovations that we avail today. Consumers rely on the portability of cell phones to access all kinds of network and applications and thereby, control all other devices. We can only look forward to the new possibilities that mobility conjures.
























