The State of LTE in 2017

According to a recent report by Ericsson, more than 540 million people would have switched over to a VoLTE network by the end of 2017. With LTE on the rise, the telephone ecosystem is propelling towards new growth zones.
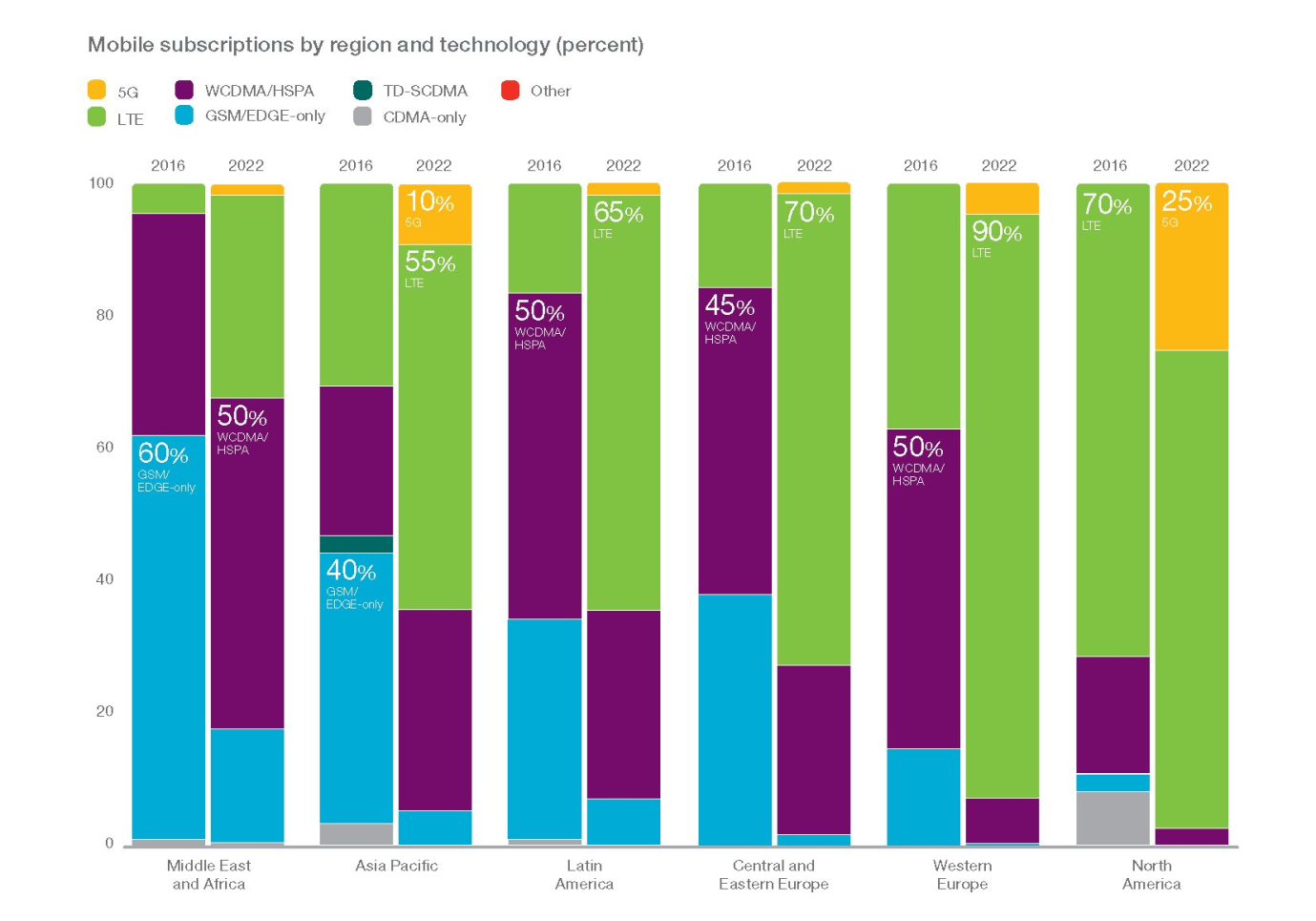
This is accompanied by an exponential usage of smartphones that support the LTE technology. Across the world, increasing consumers are on the lookout for versatile data-intensive applications. More sophisticated devices are high on demand because they are compatible with this new technology.
LTE exclusively supports higher data volume and faster network connectivity. It enables operators to deliver high-quality voice calls and data services across several devices. As a result, more and more users are conveniently sharing files, streaming live audio/video, engaging in real-time communication, social media networking, face timing, etc. This is fuelled by larger device screens, higher resolution and better platforms that support faster streaming, as per Ericsson reports.
The Explosive Growth of Internet Traffic
These developments have significant implications for global mobile internet traffic. The report demonstrates that there has been an impactful growth in data traffic that grew by 70 percent between Q1 2016 to Q1 2017.
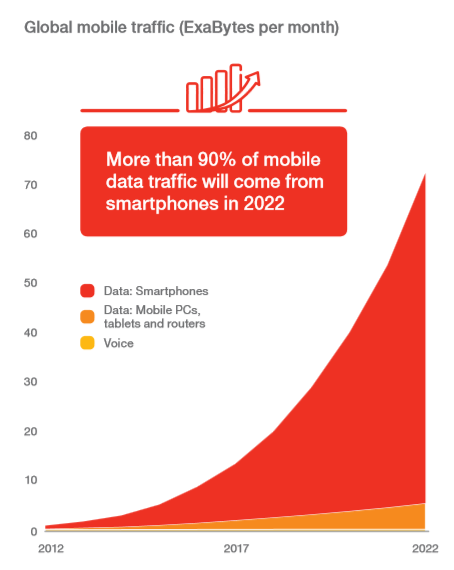
Subsequently, the report also observes emerging patterns regarding data consumption and how subscribers use their devices. It also underlines the growing popularity of VoWi-Fi calling and hints towards possibilities that network operators may explore to extend their voice services.
Vo-WiFi is a by-product of VoLTE and runs on the core IMS network. The former has vast prospects for mobile Network operators who have begun looking at it in terms of quality voice calling.
The most significant benefit of these new technologies, especially Vo-Wi-Fi can be reaped on the ‘voice calling’ front. Perhaps, we can begin to anticipate substantial improvements in the voice calling experience.
Delivering an Enhanced Voice Calling Experience
Everybody wants to communicate without hassles, and this has been the core premise of telecommunication. Calls are often interrupted due to poor network connectivity, and before VoLTE, network resources were quickly eaten up on a 3G network.
With VoWiFi, subscribers would not have to continually depend on the stability of a network to complete their conversations. This is because voice calls and messaging will be transferred on to existing Wi-Fi networks allowing subscribers to make and receive high-quality phone calls.
WiFi enabled calls are a promising ground for network operators who can tap significant revenue opportunities. They can mainly tackle the problem of indoor network coverage wherein it often becomes difficult for networks to penetrate homes. Considering that most calls are made indoors, operators can make use of this habit and translate calls into Wi-Fi calling to enable a steady communication.
How it Voice over WiFi different?
Calls operated over WiFi can reduce operating costs because the call placed upon their network would be carried over to the user’s internet/broadband.
This is fundamentally different from an OTT enabled voice calls because VoWiFi doesn’t require users to open an app.
Therefore, the call quality is in no way compromised while at the same time avoiding the chances of a call being dropped. Most importantly, the operator remains in-charge of the entire process and provides a better calling experience than OTT-generated VoIP.
With the growing movement towards VoLTE and VoWifi, we can begin to anticipate greater stronghold for operators over OTT applications.
With the new network being backed by more smartphones and devices, people would increasingly prefer quality calls at lower costs, especially ones that do not require both parties to necessarily have the same app.
Network providers and VAS players can take note of this significant evolution and work towards devising solutions or services that further assist the users.
What to expect on a global front?
However, the report takes into account significant differences in traffic levels across markets, regions, and operators.
It is to be noted that North America and Western Europe have the highest total traffic volume against user subscription. This is attributed to higher penetration of high-end user devices and well- built out LTE networks, accompanied by affordable schemes that offer large volumes of data.
On the other hand, as the most populous region, Asia Pacific has the largest share of mobile data traffic despite the slow uptake of LTE network in less developed countries. Countries like South Korea, Japan, Singapore and Hong Kong are witnessing higher adoption.
This is followed by the region extending over Central and Eastern Europe, Middle East and Africa, which are set to experience an eleven-fold increase of LTE adoption by the end of 2022. It is worth noting that more than 50 percent of the world’s population (Ericsson report) does not have access to the internet and the focus must be primarily on improving mobile network infrastructure.
On the brighter side, on an average, we have more than one million broadband subscribers being added every year, and the key drivers are increasing digital skills, decreasing smartphone prices and continued deployment of 3G and 4G broadband technologies (Ericsson)
The steady implementation of LTE across the world can also tackle hefty roaming charges overseas by offering bundled services. The seamless connectivity between WiFi and Cellular IP networks can enable calls anywhere without being reliant on the network while reducing costs for both the user and operator. We will witness a fundamental shift in the international calling process.
Wrapping Up
This development towards LTE technology is on the verge of bringing forth major implications for telecom carriers. With mobile networks being seen in a new light, operators are on their toes catching up with more dynamic, sophisticated technologies while they redefine the voice calling experience.
























